What is my gut microbiome?
There are 39,000,000,000 microorganisms living in our body, which accounts for up to 3% of our body mass. This internal vast world that is yet to be explored, mostly consisting of the bacterial phyla Firmicutes and Bacteroidetes, is not just a passive resident but an active participant in your life, influencing everything from nutrient absorption and immune responses to mood regulation and energy levels.
How is my microbiome formed? The Birth of Your Microbial Universe
Our journey begins at birth, where the initial mode of delivery—vaginal or cesarean—introduces us to our first microbial settlers, and milk from the breast delivers microbes to the gut. These events mark the start of a lifelong symbiotic relationship with our microorganisms. As we navigate through life, factors such as diet, environment, and medical treatments further sculpt our microbiome.
What does my microbiome influence? A Keystone of Human Biology
The human microbiome, with its vast genetic diversity, is beginning to be recognized as a critical organ in its own right, controlling essential functions in our body. These microbes facilitate the breakdown of complex polysaccharides, enabling the absorption of nutrients that would otherwise be indigestible. The gut microbiome also plays a crucial role in breaking down dietary fibers, producing short-chain fatty acids essential for colonocyte energy and influencing satiety, cholesterol levels and glucose metabolism. Additionally, they are key players in synthesizing essential vitamins including B12, K, biotin, and folate and bioactive compounds, influencing metabolic processes, and even fat creation and energy balance.
Furthermore, the microbiota is instrumental in educating and regulating the immune system. In fact, an astounding 70% of the immune system exists within the gut, maintaining a balance between tolerating harmless substances and defending against harmful pathogens. Disruptions in the microbiome have been linked to a myriad of health issues, including obesity, diabetes and mental health conditions.
A New Era of Genetic and Microbial Insight
The revelation that our understanding of the microbiome follows closely on the heels of a genetic revolution in medicine is no coincidence. This revolution, heralded by the sequencing of the human genome, has paved the way for next-generation sequencing technologies. These advancements have made it faster and more affordable to sequence all the genetic material in a sample, such as a stool sample, from any individual. This leap in technology has provided us with the tools to explore the microbiome's complexity, revealing an unexpected diversity and leading to the microbiome revolution in scientific research. It has allowed researchers to map the microbiome's extensive genetic landscape, which includes over two million genes, far surpassing the 20,000 to 25,000 genes in the human genome.
This groundbreaking insight underscores the microbiome's profound influence on our health and susceptibility to diseases. For healthcare professionals, this means being able to tailor treatments specifically to individuals, leading to more personalized and effective healthcare strategies. Imagine targeted probiotics and nutrional guidenece. Additionally, it opens the door to enhanced diagnostic tools for early disease detection and more precise interventions. General and personal microbiome knowledge will empower us to make informed decisions about our health based on this ecosystem within us.
How can I improve my gut microbiome? A Key to Individualized Health
Maintaining microbial health demands a conscious effort to nurture our inner ecosystem through diet, lifestyle, and mindful medical interventions. A diet enriched with diverse fibrous plants and fermented foods fosters microbial diversity, promoting a resilient microbiome. As research unfolds, the potential for microbiome-centered therapies expands, promising innovative treatments for a broad spectrum of conditions.
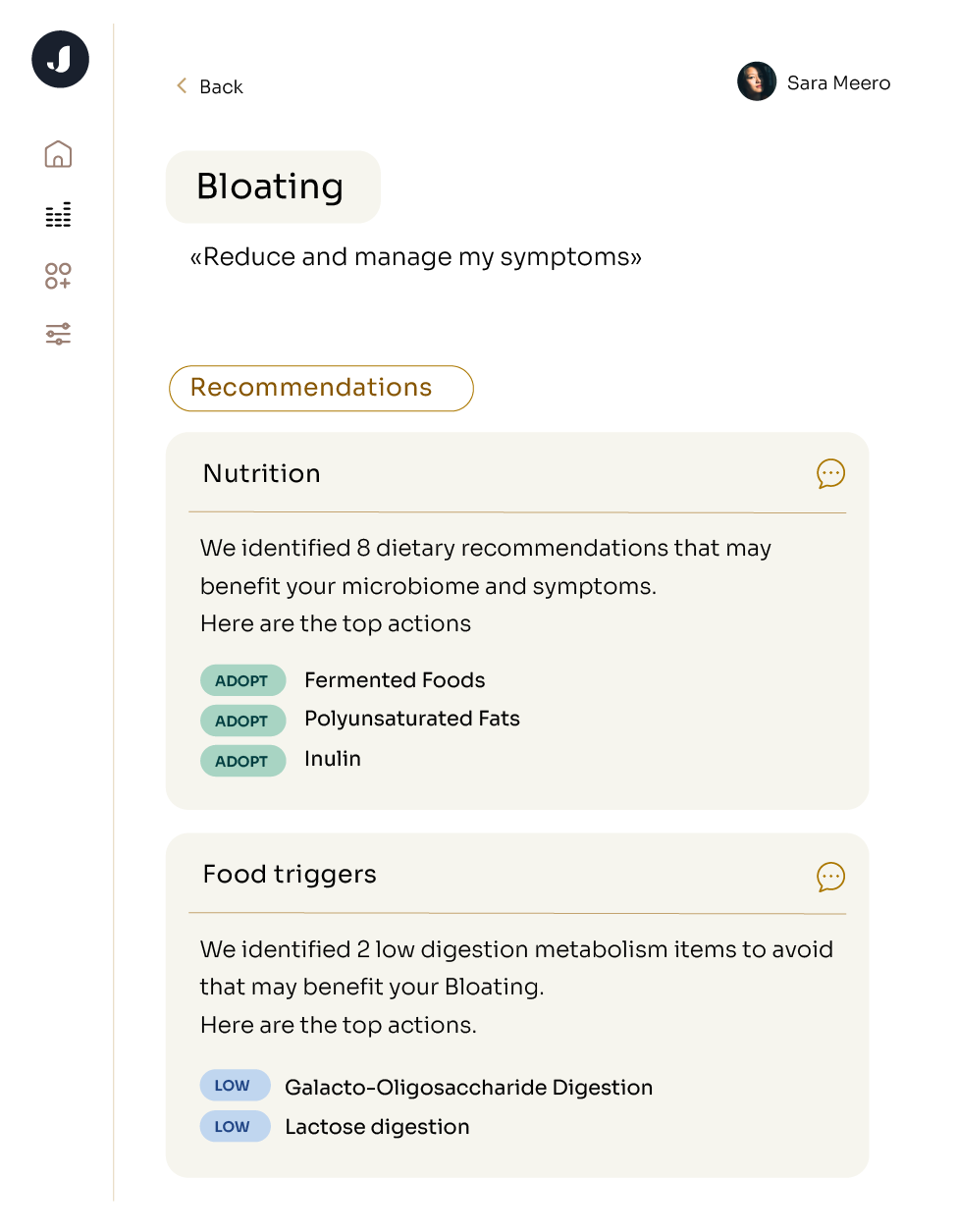
As you can see, understanding your microbiome can help you make more informed decisions about your health. Thankfully, research and understanding of the microbiome is rapidly growing with over 2,000 new articles published every month, and thanks to technological advancements, testing your microbiome is more possible now than ever. The Jona Microbiome profiling kit combines in-depth gut health testing with AI that has read through the scientific literature to provide detailed insights into the composition and health of your microbiome. By identifying specific bacterial populations and their functions, microbiome testing can guide personalized diet plans, and lifestyle changes to improve overall health and prevent or manage diseases more effectively.